WiFi signal or WiFi range issue with Windows 10 is pretty common among users. Along with and apart from weak WiFi signal, users may face several other issues related to WiFi. These issues include slow WiFi speed, WiFi connection dropping regularly, not being able to connect to WiFi automatically, etc. In this article, we are going to look at the solutions to boost weak WiFi signal on Windows 10. These methods may also work well for other WiFi range or signal related issues on Windows 10.
Added profile information for Windows 10, version 1703, and clarified how roaming profile versions work when upgrading operating systems - see Considerations when using Roaming User Profiles on multiple versions of Windows. Customer feedback. March 14th, 2017: Added optional step for specifying a mandatory Start layout for Windows 10 PCs. There, in the list named Property, look for Roaming Sensitivity Level, Roam Tendency, or Roaming Aggressiveness. Select it when found, and from the Value drop-down, select the Aggressive option. Step 4: Now, in the list, select the Antenna Diversity option, and change its value to Auto. Step 5: Look for Band Preference or BSS Mode. Apr 20, 2017 Windows 10 supports Fast BSS Transitions over networks using 802.1X as the authentication method. Pre-Shared Key (PSK) and Open Networks are currently not supported. With the combination of 802.11k, 802.11v, and 802.11r, Windows 10 takes advantage of established industry standards to improve the roaming experience for our users.
What are the reasons that may lead to weak WiFi signal on PC? At times the Windows 10 updates may cause the issue. Outdated WiFi Driver, issues with WiFi card, and some internal setting might be the leading reasons for the same.
One of the ways to check if the WiFi range issue is actually there with your PC is through comparison. See if
Let us see how to boost WiFi signal on laptop or PC on Windows 10.
How to Fix Weak WiFi Signal on Laptop and PC
There are several simple, as well as complex methods involved that will help you fix weak WiFi signal on Windows 10 PC.
#Solution 1 – Maximize WiFi Adapter Performance to fix weak WiFi signal in Windows 10
Maximizing performance of WiFi Adapter from medium to maximum can be helpful. The WiFi adapter is set to work on medium performance. Follow these steps:
Step 1: Press Windows button, and in the Start search bar, type Power Options. Select Power Options from the search menu.
Step 2: In the new window that opens, click on the Change plan settings of the power plan you are using.
Step 3: Click on the Change advanced power settings.
Step 4: A new window opens. Here, look for Wireless Adapter Settings. Click on it to expand. Then expand the Power Saving Mode. If you are on a desktop, you will see just one option, named Setting. If on a laptop, you will see On battery and Plugged in options. Click on the option(s) and select the Maximum Performance option. When done, click on Ok to apply the settings.
See if this method worked to increase WiFi range in Windows 10. If not, try the next method.
#Solution 2 – Set WiFi Sensibility Value to Maximum

You can set your WiFi Sensibility value to highest capacity and change a couple more settings in order to boost WiFi signal on laptop or PC running on Windows 10. Here’s what to do:
Step 1: Press Win + X keys on your keyboard. From the menu, click on Device Manager.
Step 2: From the list of device drivers in Device Manager, find your WiFi driver. Right click on it and select the Properties option.
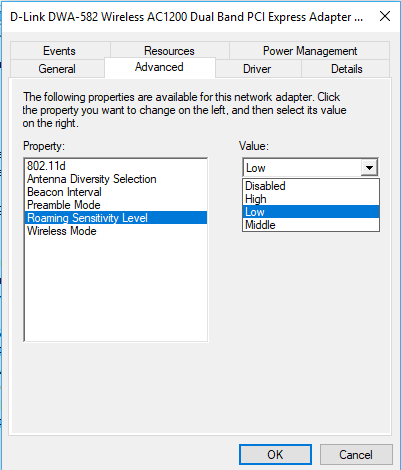
Step 3: In the Properties window, go to the Advanced tab. There, in the list named Property, look for Roaming Sensitivity Level, Roam Tendency, or Roaming Aggressiveness. Select it when found, and from the Value drop-down, select the Aggressive option.
Step 4: Now, in the list, select the Antenna Diversity option, and change its value to Auto.
Step 5: Look for Band Preference or BSS Mode. If using a 5G connection, set the value to 802.11a. If using a normal 2.4GHz connection, set the value to 802.11g or 802.11b.
Note: The 802.11a value will only be available if your WiFi card supports 5G.
Step 6: Once done changing these values, press on Ok to apply the settings. After that, restart your PC.
See if making these changes helped to boost weak WiFi signal on your Windows 10 PC. If nothing changed, give the next method a try.
#Solution 3 – Change WiFi MTU
You can try to change the MTU value of your WiFi adapter. Here’s how to do it:
Step 1: Press Windows + X and click on Command Prompt (Admin) in the menu that opens.
Step 2: In Command Prompt window, type netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces and press Enter. Note down the name of your WiFi adapter that appears. It could be Wireless Network Connection or Wi-Fi.
Step 3: In the command prompt window, type the command given below
Now press Enter.
Note: If your Wi-Fi network adapter name is different , then replace Wi-Fi with a different name in above code.
To know, your WiFi adapter name, do this:-
- Search View Network Connections in Windows 10 search box. Click on search result.
- Note down the Wi-Fi name.
In the screenshot given above, the WiFi name is Wi-Fi
Additional Steps
In Command Prompt, type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter.
type netsh winsock reset catalog and press Enter.
type netsh int ip reset and press Enter.
#Solution 4 – Update WiFi Driver
If the WiFi Network Driver on your PC is outdated or faulty, it may be causing all the trouble. You can try to update the WiFi driver as the first method to fix weal WiFi signal on Windows 10 laptop or PC. Follow the steps given below:
Step 1: Press the Windows + X keys on your keyboard. From the Win +X menu, click on Device Manager.
Step 2: Device Manager will open with the list of drivers. Look for the Network Adapters dropdown in the list of drivers. Click the Network Adapters option to expand it, then locate the Wireless internet driver. Do a right click on the WiFi driver and click on the Update driver software option.
Step 3: In the Update Driver window that opens, click on the Search automatically for updated driver software option. Your PC will begin looking for an updated version of the WiFi network driver. After a new version is found, the WiFi driver will be updated.
Restart your PC to complete the update process. If your driver is already updated to the latest version, or if the update didn’t fix weak WiFi signal on your PC, try the next method.
#Solution 5 – Check WiFi Card for Issues
If you use a PC, you must give your WiFi network card a check. Sometimes it’s the WiFi card that causes the issues. If the WiFi card is loosely connected to your PC, or if there’s dust accumulated on the card and connecting ports, it can lead to a weak WiFi signal. Try to reconnect the WiFi card to see if that works.
And old WiFi card could also be the reason why your PC is not getting enough WiFi signal. You can replace your PC’s WiFi card if you think its too old.
Are you not aware of what a WiFi card is or are not familiar with your PC’s hardware? Get help from someone who is an expert in PC hardware.
In the end,
if nothing is working, and you haven’t changed your WiFi card, try changing it to a new one. Additionally, you can buy Wi-Fi extenders which can be found online which increases the range of WiFi routers.
Related Posts:
Access Points
To understand what roaming is, you first have to know what device makes the software function necessary.
If you are only used to household internet setups, the idea of roaming might be a little strange to think about. In your house you have your router, which you connect to, and that’s all you need to do. You may have the option of choosing between 2.4GHz and 5GHz channels, however that’s as complicated as it can get.
Now imagine that your house is very large, let’s say the size of UMass Amherst. Now, from your router in your living room, the DuBois Library, it might be a little difficult to connect to from all the way up in your bedroom on Orchard Hill. Obviously in this situation, the one router will never suffice, and so a new component is needed.
An Access Point (AP for short) provides essentially the same function as a router, except that multiple APs used in conjunction project a Wi-Fi network further than a single router ever could. All APs are tied back to a central hub, which you can think of as a very large, powerful modem, which provides the internet signal via cable from the Internet Service Provider (ISP) out to the APs, and then in turn to your device.
On to Roaming
So now that you have your network set up with your central hub in DuBois (your living room), and have an AP in your bedroom (Orchard Hill), what happens if you want to go between the two? The network is the same, but how is your computer supposed to know that the AP in Orchard Hill is not the strongest signal when you’re in DuBois. This is where roaming comes in. Based on what ‘aggressiveness’ your WiFi card is set to roam at, your computer will test the connection to determine which AP has the strongest signal based on your location, and then connect to it. The network is set up such that it can tell the computer that all the APs are on the same network, and allow your computer to transfer your connection without making you input your credentials every time you move.
What is Roam Aggressiveness?
The ‘aggressiveness’ with which your computer roams determines how frequently and how likely it is for your computer to switch APs. If you have it set very high, your computer could be jumping between APs frequently. This can be a problem as it can cause your connection to be interrupted frequently as your computer authenticates to another AP. Having the aggressiveness set very low, or disabling it, can cause your computer to ‘stick’ to one AP, making it difficult to move around and maintain a connection. The low roaming aggression is the more frequent problem people run into on large networks like eduroam at UMass. If you are experiencing issues like this, you may want to change the aggressiveness to suit your liking. Here’s how:
How to Change Roam Aggressiveness on Your Device:
First, navigate to the Control Panel which can be found in your Start menu. Then click on Network and Internet.
From there, click on Network and Sharing Center.
Then, you want to select Wi-Fi next to Connections. Note: You may not have eduroam listed next to Wi-Fi if you are not connected or connected to a different network.
Now, select Properties and agree to continue when prompted for Administrator permissions.
After selecting Configure for your wireless card (your card will differ with your device from the one shown in the image above).
Finally, navigate to Advanced, and then under Property select Roaming Sensitivity Level. From there you can change the Value based on what issue you are trying to address.
Tx Power Level
And that’s all there is to it! Now that you know how to navigate to the Roaming settings, you can experiment a little to find what works best for you. Depending on your model of computer, you may have more than just High, Middle, Low values.
What Is Roaming Sensitivity Level
Changing roaming aggressiveness can be helpful for stationary devices, like desktops, too. Perhaps someone near you has violated UMass’ wireless airspace policy and set up and hotspot network or a wireless printer. Their setup may interfere with the AP closest to you, and normally, it could cause packet loss, or latency (ping) spiking. You may not even be able to connect for a brief time. Changing roaming settings can help your computer move to the next best AP while the interference is occurring, resulting in a more continuous experience for you.